
To apply these changes, restart the SSH service: sudo systemctl restart sshd However, even if you connect without a password, root login is not recommended: if keys are compromised, your entire host is compromised.Īs a consequence, you can set this option to “ no” in order to restrict it completely.Īgain open the SSH server config file on Debian 11: sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_configįind the line below and set it to no: PermitRootLogin no In short, you need to set up SSH keys and use them in order to connect as a root.
This option means that all interactive authentication methods are banned, allowing only public keys to be used. Disable Root Login on your SSH Serverīy default, on recent distributions, root login is set to “prohibit-password”. Note: Be careful when you change your default SSH port, you will have to specify it when connecting to it. When you are done, save and close the file. Open the sshd_config file with your favorite text editor, here we use vi: sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_configįind the port line, and change it to your desired value, here we change it to 2222: Port 2222 To secure your SSH server, it’s recommended to change the SSH default port on Debian 11. In this tutorial, we are going to focus on the server part of the configuration. It is used for example to define the reachable SSH port or to deny specific users from communicating with your server.

Process: 1160 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)

Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ssh.service enabled vendor preset: e>Īctive: active ( running) since Sat 05:34:51 EST 3s ago ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server.When your installation is completed, enable your service to start on boot: sudo systemctl enable ssh Check SSH StatusĬheck your SSH status with the command below: sudo systemctl status sshd
#Debian enable ssh install
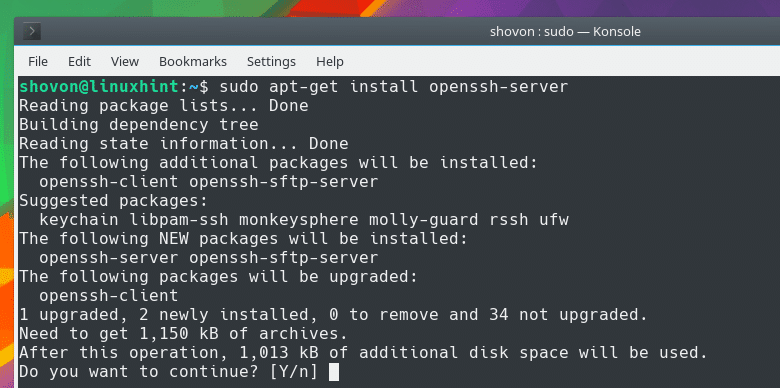
Then, use the command below to install OpenSSH: sudo apt install openssh-server Note: This information does not mean that you have an SSH server running on your server, it only means that you are currently able to connect as a client to SSH servers. To verify this, run the command below: ssh -V Output
#Debian enable ssh update
Verify SSH Installation on Debian 11įirst, you need to update your local package index with the command below: sudo apt updateīy default, SSH is installed on Debian 11. To do this, you can follow our guide the Initial Server Setup with Debian 11. To complete this guide, you must log in to your server as a non-root user with sudo privileges and set up a basic firewall. Steps To Enable and Configure SSH on Debian 11


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
